Rotary Wing Aircraft - A helicopter or rotary-wing aircraft is a heavier-than-air aircraft with wings or rotor blades that rotate around a vertical mast. A number of rotor blades mounted on a mast is called a rotor. The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) defines a helicopter as assisted in flight by the wind reaction of one or more rotors.
Rotorcraft generally includes one or more rotors. Includes aircraft that carry entire tires in flight, such as autogyros and gyrodynes. A hybrid helicopter is a helicopter with additional thrust tubes, fans, or increases the rotor with static lift surfaces. Some types, such as helicopters, are capable of vertical take-off and landing. An aircraft that uses rotor lift for vertical flight but only swaps fixed wings for horizontal flight is a convertible, not a helicopter.
Rotary Wing Aircraft

A helicopter means that the helicopter is vertical; to soar before Next, sideways A helicopter powered by engines throughout flight to allow vertical landing. Helicopters have many different configurations of single or multiple main rotors.
Bell's Plan To Finally Realize A Rotorcraft That Flies Like A Jet But Hovers Like A Helicopter
Helicopters powered by a single main lift rotor, tail rotor, Some form of anti-torque device such as a propeller or NOTAR is required; Except for a few rare examples of helicopters using tip jet thrust, there is almost no torque.
An autogyro (sometimes called a gyrocopter, gyroplane, or gyroplane) uses an aerodynamically driven unpowered rotor in automatic mode to develop lift and a powered propeller similar to a fixed wing for thrust. . An autogyroscope rotor is similar to a helicopter rotor, but air must flow upward through the rotor disk to accelerate rotation. Early autogyros were in the form of a tractor with wings to pull the aircraft into the air. Similar to early autogyros. Later model autogyros have a rear-mounted engine and propeller in a pusher configuration.
The Autogyro was built in 1920 by Juan de la Cierva. The pusher autogyro was first tested with the Buhl A-1 Autogyro by Etine Dormoy.
A gyrodyne's rotor is usually powered by its engine for takeoff and landing—it hovers like a helicopter—with torque and forward thrust provided by one or more propellers on short, thick wings. As propeller power increases, the rotor has less power to provide forward thrust, resulting in pitch and rotor blade slippage. At cruising speed where most or all of the thrust is provided by the propellers; The rotor only gets enough power to maintain lift by pulling the airfoil. The effect is a more efficient helicopter in autorotation than an autogyro freewheel, reducing the negative effects of helicopter rollback at high airspeeds.
The Evolving Role Of Rotary Wing Platforms In The Integratable Carrier Air Wing
A rotor kite or gyroplane is an aircraft that rotates with wings without an engine. Like an autogyro or a helicopter. It relies on lift generated by one or more sets of rotors for flight. Unlike a helicopter, Autogyros and rotor kites do not have a genie to power the rotors, but an autogyro has a thrust engine that moves the rotor forward while it spins. A rotor kite has no genie at all and depends on whether you carry them. Dropped from another plane or pulled into the air behind a car or boat.
A rotary wing is characterized by the number of blades. Typically this is between two and six per drive shaft.
Some rotary wing aircraft are designed to stall the rotor in forward flight like a rotary wing. In vertical flight and hovering it rotates as a rotary vane or rotor and stops to act as a fixed wing to provide some or all of the lift required in forward flight at speed. Additional fixed wings can also be used to provide stability and control.

An early American proposal was to convert the Lockheed F-104 Starfighter to a triangular rotor wing. Hughes later reconsidered the idea.
Rotary Aircraft: The Problem With Making Bigger Better
In 1986, the Sikorsky S-72 Rotor Systems Research Aircraft (RSRA) was equipped with a four-bladed rotor known as the X-wing. The program was canceled two years before the rotorcraft flew.
Later, the canard rotor/wing (CRW) concept incorporated both a "canard" noseplane and a conventional tailplane that carried the rotor wing and provided control during forward flight. vertical In low-speed flight, the main airfoil, like a helicopter rotor, is wing-driven by jet engine exhaust and does not require a tail rotor. In high-speed flight, The wing rests in the open position, like the main wing of a triplane, and the gin exits through a normal jet nozzle. Two Boeing X-50 Dragonfly prototype twin-seater helicopters have been flying since 2003, but both programs have been scrapped after failed conversions.
In 2013, the US Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) published a vertical-to-horizontal flight transition method and related technology on December 6, 2011.
The design uses high alpha airflow to ensure symmetrical airflow between all rotor blades so it must drop almost vertically during transition.
What You Need To Know About Rotary Wing Aircraft Insurance
Another approach proposes a tail-mounted design in which the elevator surfaces act as rotors during takeoff; The ship tilts to flight level; A rotor stall is proposed to act as a fixed wing. The U.S. military is planning a sortie within a year. And some of the biggest names in the defense industry are trying to win it.
Last year, the military put out a call for tenders, known as an RFP, as the first step in its Joint Multi-Role Technology Demonstration (JMRTD) program, and the competition included two efforts: Bell Helicopter's V-280 "Valor" and Boeing and Lockheed-Martin's SB-1 "Defiant." The two designs are JMRTD's. Different approaches have been taken to meet performance requirements; This includes the ability to reach an airspeed of 230 knots and a combat radius of about 275 miles. The Valor was a tiltrotor aircraft based on Bell's experience and learnings with the V-22 “Osprey” and the Defiant was a co-axial rotor design using two counter-rotating rotors and a stern thruster on top of the fuselage.
The two designs take different approaches to meet JMRTD's performance requirements; This includes the ability to reach an airspeed of 230 knots and a combat radius of about 275 miles. The Valor was a tiltrotor aircraft based on Bell's experience and learnings with the V-22 “Osprey” and the Defiant was a co-axial rotor design using two counter-rotating rotors and a stern thruster on top of the fuselage.
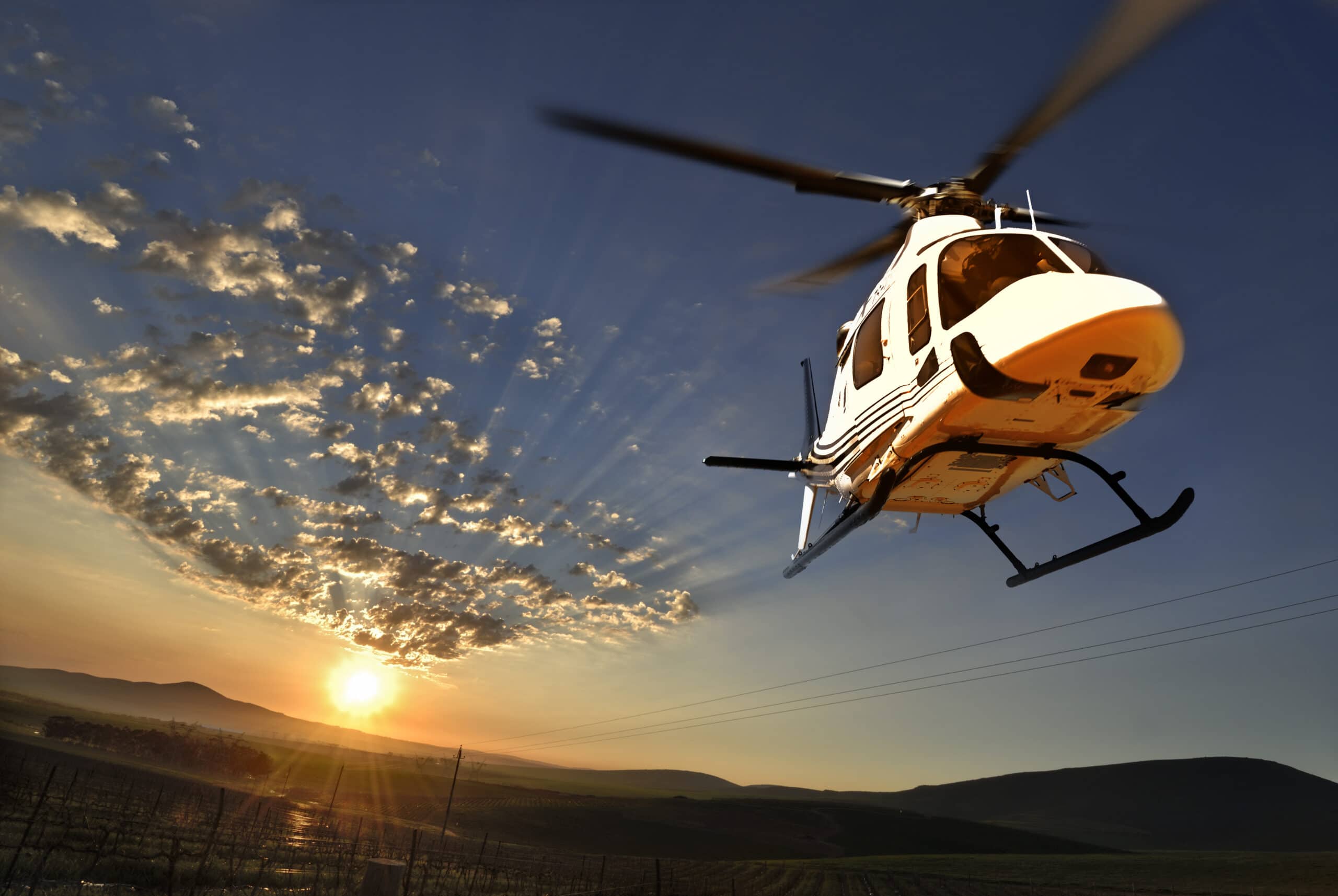

"We understand that there is still a filter in the murky history of the tilt engine," said Robert Hastings, Bell's vice president of communications and government affairs. “But the Marines will tell you that you've been transformed. Young pilots who had never learned bad habits from other airplanes were flying the V-22 in ways we had never imagined.
Ch 47 Chinook Rotary Wing Aircraft Hi Res Stock Photography And Images
Hastings, who flew Cobras and Blackhawks in the Army and served as assistant defense secretary for public affairs during Robert Gates' tenure at the Pentagon, recalled talking to a V-22 squadron commander at the last Singapore Air Show. . At this time he had Australia, Okinawa and the Philippines have bees; displayed.
"He's a lieutenant colonel in the same field as an admiral a generation ago," Hastings said. "The V-22 not only changes the way we operate," he quoted Gen. Davis, deputy commandant of the Marine Corps. The enemy has changed the way he worries about us.
But Hastings was quick to point out that while the V-22's successes in the country's most recent conflicts, including how the Air Force's Special Operations Command used the CV variant, the V-280 is what it calls it. Clean page design."
When making the Osprey, Hastings explained that digital designs and more precise machining allow parts to "slide well" without having to be sandblasted by assembly technicians. With these kinds of improvements, Bell aims to make the V-280 cost about half the $71 million unit cost of the V-22.
How Tough Is The Transition To Helicopters
Bell has partnered with Lockheed-Martin to provide the Valor with a state-of-the-art cockpit based on what engineers and test pilots learned during the development of the F-35. A helmet visor insignia (a challenge to develop during F-35 testing) is not planned, but the cockpit's "open architecture" could allow V-280 pilots the option in the future, Hastings said. The cockpit also houses several sensors and mission packages designed to provide the Valor with much of its combat power.
Bell calls their JMRTD candidate a "third generation" tipper. (V-22 is
Rotary wing aircraft mechanic jobs, flight performance of fixed and rotary wing aircraft, army rotary wing aircraft, difference between fixed wing and rotary wing aircraft, aircraft wing, fixed and rotary wing aircraft, rotary wing aircraft definition, rotary wing aircraft for sale, aircraft wing desk, fixed wing aircraft vs rotary, rotary aircraft, rotary wing